Light, Shadow and Reflection
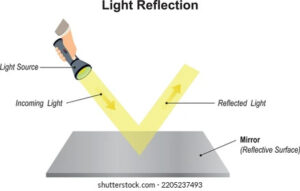
Image Credit: https://www.shutterstock.com/search/light-reflection-experiment
LIGHT
Light is a form of energy that enables every living being to see the objects around them.
Source of light
A source of light can be anything. Light can be emitted from the sun, and the stars, as well as from a bulb.
Luminous object: The objects which emit their own light is called luminous objects. For ex: Sun, torch and bulb.
Non-Luminous object: The objects which do not emit their own light is called non- luminous objects. For ex: Moon
TYPES OF MATERIAL TRANSMIT LIGHT
- Transparent objects
- Translucent objects
- Opaque objects
Transparent objects: These objects allow light to pass through them in straight line. Example: water
Translucent objects: These objects allow light to pass through them partially. Example: tissue paper, butter paper
Opaque objects: These objects do not allow light to pass through them. Ex: wall, trees and table.
Characteristics of light
- Light travel in a straight line.
- Light is a transverse wave and does not need any medium to travel.
- Light can also travel through the vacuum.
Shadow
A shadow is a dark shape that is formed when an object blocks a source of light.
Properties of shadow
- The objects must be opaque or translucent.
- It is dark in color .
- Transparent objects do not make shadow.
- They are formed opposite to the source of light.
Pinhole camera
A pinhole camera is a simple camera with no lens but with a tiny aperture. That aperture is known as a pinhole.
Properties of pinhole camera
- Image formed in pinhole camera is inverted.
- Image converted in pinhole camera is smaller in size.
Rectilinear propagation of light
Light travel in a straight line is called rectilinear propagation of light.
- Ray of light: It is a path along which light travel in the given direction.
- Beam of light: Bunch of rays of light travel in the given direction.
Mirror
A mirror is a polished surface which can make the image.
Types of mirrors
- Plane mirror: A plane mirror can be defined as a mirror that is flat on the surface and is without any inward and outward curve. They can easily reflect light in various directions.
- Concave mirror: A concave mirror is also known as converging mirror. Its reflecting character is to converge light rays toward one particular point of focus.
- Convex mirror: A Convex mirror is also known as diverging mirror because it diverges the ray of light, which fall on its reflecting surface.
EXAM RELATED QUESTIONS
1.What are the three things required for the formation of shadow?
Ans1 Light, space and opaque objects.
2.Moon is a non- luminous object. how does it shine at night?
Ans2Moon reflects the light of the sun at night.
3.How does a light ray travel?
Ans3 Light rays travel in a straight line.
4.What material can be used to make a pinhole camera? How it can be used?
Ans.4 Pinhole camera can be made with simple material like cardboard, tracing paper etc. it can be used to image the sun and brightly lit objects.
5.Why cannot we see our image in the mirror in completely dark room?
Ans5 We cannot see our image in the mirror in completely dark room because there is no light to reflect.
6.What is the difference between luminous objects and non-luminous objects?
Ans. Objects that give out or emit light of their own are known as luminous objects e.g.: sun and candle etc. Objects that cannot give out or emit light of their own are known as non-luminous objects. Such as book and chair.
7.Why cannot we see objects through T shaped and N shaped pipe?
Ans. We cannot see objects through T shaped or N shaped pipe because light travel through straight line.
8.What do you mean by scattering of light?
Ans. When a beam of light falls on a rough surface it is turned back in different directions. It is called scattering of light.
9.What is umbra?
Ans. Umbra is the dark region behind an object facing light, which receives no light at all.
10.What is an incandescent body? Give an example
Ans Incandescent bodies emit light when heated to a very high temperature. An example is an electric bulb.
