ELECTRICITY AND CIRCUIT
Electricity
It is a form of energy made up of charges that can produce light, heat or motion.
What causes an electrical charge?
It is caused by an imbalance in positive or negative charge.
Sources of electrical energy
Solar energy: electricity produced by sunlight
Wind energy: electricity produced by wind speed.
Hydro energy: electricity produced by water.
Electric current
Electric current refers to the flow of electricity in an electronic circuit.
The SI unit of current is Ampere
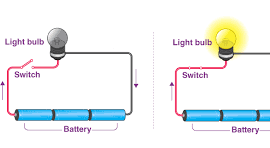
Image Credit: https://byjus.com/physics/electric-circuit/
Source of electric current
It is a device which is used to produce an electric current is called a source of electric current.
Common source of electric current are cells, generators and batteries which comes in various shape and size
Electric circuit.
Electric circuit is the path of conduction wires through which current flow
Some electric circuit in the natural world: lightning
Some man- made electric circuit are: wiring that lights our house.
Types of circuit
- Closed circuit
- Open circuit
Closed circuit: An electric circuit which has a closed loop through which current can flow is called a closed circuit. If the circuit is complete or closed, the bulb lights up.
Open circuit: An electric circuit in which there is a gap or break and disallow the flow of current is called an open circuit. A bulb will not light up if there is a gap in a circuit.
Components of electricity
Connecting wires: It helps to conduct the electric current and complete the circuit.
Bulb: An electric bulb is a device which glows and emits light, when electric current passed through it.
Battery: It is a series combination of two or more cells.
Switch: A switch works by breaking or completing the circuit path.
Electric cell or dry cell: An electric cell has two terminals; one is called positive while the other is negative. Inside the electric cell, the electric charges flow from negative terminal to the positive terminal.
Conductor and Insulator
Conductor: The Materials which allow the electric current pass through it, is known as conductor. Silver, copper, aluminium and irons are conductor.
Insulator: The materials which do not allow electric current to pass through it, is known as insulator. Rubber, wood, paper, glass and plastic are insulator.
Filament
In electric bulb, there is a thin tiny wire inside the glass cover. This is called filament.
EXAM RELATED QUESTIONS
1.What is the direction of flow of current in a dry cell?
Ans. The current flows in a closed circuit from +ve(positive) to -ve(negative) terminal of the cell.
2.What is solar cell?
Ans. A device which converts solar energy into electric energy.
3.Give one difference between a cell and a battery?
Ans. A cell is a single unit that produce electricity, while a battery is a collection of a cells.
- A fused bulb does not glow. why?
Ans. Fused bulb means a bulb in which filament is broken and hence the circuit becomes incompletes therefore it does not glow.
- What is the name of thin wire in the electric bulb?
Ans. The thin wire in an electric bulb is called the filament.
- Why should you not touch electric appliances and switches with wet hands?
Ans. Wet hands can conduct electricity and increase the risk of electric shocks when touching electric appliances and switches.
7.What is dry cell?
Ans. It is a device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
- Mention any two advantages of dry cell?
Ans. It convert chemical energy into electric energy.
It is light and small in size.
9.Name the scientist who invented electric cell and the scientist who invented electric bulb?
Ans. Electric cell: Alessandro Volta
Electric bulb: Thomas Alva Edison
10.Why is copper wire usually covered with rubber or plastic?
Ans. Rubbers and plastic are insulator. They prevent short circuiting and electric shocks
If by mistake any living things comes in contact with the wires.

