MICROORGANISMS: FRIEND AND FOE
MICROORGANISMS
Living organisms that cannot be seen with naked eyes are called microorganisms as they can be seen with the help of microscope, they are called microscopic organisms.
These are classified into 4 major groups:
Bacteria, Fungi, Protozoa and Algae.
Classification of Microorganisms
- Bacteria
- Bacteria are single celled microorganism.
- They can be seen only under a microscope.
- Found in wide range of habitat ranging from glaciers to deserts and hot springs.
- For example: Curd bacteria (Lactobacillus).
- Fungi
- The Fungi are a group of eukaryotic microorganisms.
- Lack chlorophyll and are generally found in colonies.
- For example: Penicillium
- Protozoa
- Unicellular or multicellular microorganisms.
- Usually found in water.
- For example: Amoeba and Paramecium.
- Algae
- Algae are photosynthetic organisms that possess photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll.
- For example: Spirogyra
- Viruses
Viruses are also microscopic which reproduce only inside the cells of the host organism, which may be a bacterium, plant or animal. For example: Influenza virus, polio virus.
Food preservation
Salts, Sugar, edible oils and vinegar are the common chemicals generally used to check the growth of microorganisms. Therefore, they are called preservatives.
Methods of food preservation.
- Chemical methods
- The chemicals that control the growth of microorganisms on food are called preservatives. For example: Salt and edible oil.
- Common salt is used as preservatives in pickles.
- Oil and vinegar are used as preservatives in pickle and vegetables.
- Heat and cold treatment
- Boiling the milk helps in killing microorganisms present in it.
- Pasteurization is a process that involves heating liquids or foods to a temperature that kills harmful germs, then rapidly cooling them.
- Storage and packing
Dry fruits and vegetables are stored in sealed air tight packets to prevent microbial attack.
Importance of microorganisms
- In food industry
- Lactobacillus bacteria promote the conversion of milk into curd.
- Yeast is used in preparation of breads, pastries and cakes.
- In medicine production
- Microorganisms are used for the production of antibiotics and vaccines in the field of medicine.
- Microbes have proteins that can be used as vaccines against infectious diseases.
Antibiotics
- Antibiotics are the chemicals used to control or kill disease causing microorganisms.
- First antibiotic penicillin was prepared by Alexander Fleming.
- In beverage industry
- Yeast is used for commercial production of alcohol, wine and vinegar (acetic acid).
- Yeast acts on sugar and converts it into alcohol by the process of fermentation.
- Louis Pasteur discovered fermentation.
- In vaccine production
- A vaccine is a substance that is used for the production of antidotes in the body and provides immunity against some diseases.
- Vaccination helps in controlling diseases such as Cholera, Polio, Small pox etc.
- Vaccine for small pox was discovered by Edward Jenner.
- In increasing soil fertility
Blue green algae and rhizobium bacteria are called nitrogen fixers.
In cleaning the environment
Microorganisms help in converting dead waste of plants and animals into simpler substances by the process of decomposition.
Nitrogen cycle
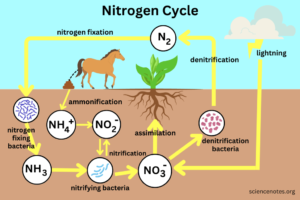
Image Credit: https://sciencenotes.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Nitrogen-Cycle.png
First process of nitrogen cycle is fixation of nitrogen gas into nitrogenous compounds caused by bacterium, rhizobium and lightning. Nitrogen compound in soil is taken up by the plants through roots and used up in synthesis of plant protein. Animals obtain nitrogen by feeding on plants. Waste of plants and animals are converted to nitrogenous compounds by the action of bacteria and fungi in the soil.
Harmful uses of microorganisms
They can be harmful in many ways to humans, plants and animals and cause diseases. The diseases causing microorganisms are known by the name of pathogens.
1 Diseases causing microorganisms in humans
- The harmful pathogens enter the body of humans by means of air, water or the food.
- The diseases that can spread form an infected person to a healthy person through air, water or food are called communicable diseases.
- The example include cholera, chicken pox and tuberculosis.
- The organisms that transmit diseases from one place to the other are called carrier.
Example of carriers
- Housefly spread diseases such as cholera, dysentery and typhoid.
- Female Anopheles mosquito spreads malaria parasites.
- Female Aedes mosquito spread dengue virus.
- Diseases caused by virus
- Chicken pox
- Polio
- Measles
- Diseases caused by bacteria
- Tuberculosis
- Cholera
- Typhoid
- Diseases caused by protozoa
- Malaria
- Sleeping sickness
- Toxoplasmosis
- Diseases in plant caused by bacteria
| Plant diseases | microorganism | Mode of Transmission |
| Citrus canker | Bacteria | Air |
| Rust of wheat | Fungi | insects and seeds |
| Yellow vein mosaic of bhindi | Virus | Insect |
Food poisoning
Microorganisms that grow on our food sometimes produce toxic substances. These make the food poisonous and result in serious illness and even death.
EXAM RELATED QUESTIONS
1 Name the group in which microorganisms are broadly classified?
Ans. Bacteria, Fungi, Protozoa, Algae.
2 Write the name of bacterium that helps in the formation of curd?
Ans. Lactobacillus.
3 Write the names of any two antibiotics?
Ans. Streptomycin
Erythromycin
4 Name a microorganism which help in nitrogen fixation?
Ans. Rhizobium.
5 Name the first antibiotic discovered?
Ans. Penicillin.
6 What is fermentation?
Ans The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is called fermentation.
7 Name some unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Ans. Unicellular organisms- Bacteria. Algae and protozoa
Multicellular organisms- Algae and fungi
8 How milk is turned into curd?
Ans. A little curd is added to warm milk to set curd. The bacterium Lactobacillus promotes the formation of curd.
9 What are the different methods of food preservation?
Ans. Different methods of food preservation are:
1 Chemical method
2 Preservation by common salt
3 Preservation by sugar
4 Preservation by oil and vinegar
5 Heat and cold treatment
6 Storage and packing
10 What are communicable diseases?
Ans. Diseases that spread from an infected person to healthy individual through air, water or direct contact is called communicable diseases.
